Employment and Social Development Canada: Operational Directive on Business Continuity Management
Table of Contents
- 1. Effective Date
- 2. Application
- 3. Context
- 4. Directive Statement
- 5. Business Continuity Management Program
- 5.2 Business Impact Analyses
- 5.3 BCP Development and Arrangements
- 5.4 Horizontal BCPs
- 5.4.1. Step 1: Develop a Critical Service Process Flow
- 5.4.2. Step 2: Identify Partners/Stakeholders
- 5.4.3. Step 3: Form a Horizontal BCP Working Group
- 5.4.4. Step 4: Assess/Prioritize Critical Functions
- 5.4.5. Step 5: Form Critical Function Sub Working Groups
- 5.4.6. Step 6: Identify Dependencies
- 5.4.7. Step 7: Develop Recovery Strategies
- 5.4.8. Step 8: Finalize Horizontal BCP(s)
- 5.5. Post-Event Recovery
- 5.6. BCM Program Readiness and Maintenance
- 6. Oversight
- 7. References
- 8. Enquiries
1. Effective date
This directive takes effect on July 4th, 2018.
2. Application
The Operational Directive on Business Continuity Management (BCM) applies to all branches and regions including programs and service delivery within the Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) Portfolio (ESD, Service Canada and Labour Program), and is in accordance with the Departmental Strategic Emergency Management Plan (SEMP), and the Policy on Government Security (PGS).
3. Context
The Treasury Board Secretariat’s (TBS) Operational Security Standard – Business Continuity Planning (BCP) Program states that departments must establish a BCM Program to provide for the continued availability of services and associated assets that are critical to the health, safety, security or economic well-being of Canadians and the effective functioning of government. Continued availability of other services and assets must be provided when warranted by a threat or risk assessment.
Note: A program or service is deemed critical if the recovery time objective to achieve minimum service levels has to occur within the initial 72 hour window, after which the availability and integrity of this service or program might be compromised and result in a high degree of injury to Canadians and government.
The Operational Directive on BCM is being implemented to ensure ESDC’s compliance with the TBS Operational Security Standard – Business Continuity Planning (BCP) Program and is to be read in conjunction with the SEMP, the Emergency Management Act, the Federal Emergency Response Plan, the Policy on Government Security and Public Safety’s A Guide to Business Continuity Planning.
4. Directive Statement
4.1. Objective
The objective of this directive is to clearly articulate the Department’s requirements for a BCM Program that will allow it to fulfill its mandate within federal legislations, policies and standards.
4.2. Expected Results
The Department will have comprehensive and consistent BCPs in place that will strengthen ESDC’s ability to maintain continuous delivery of critical operations and services to Canadians.
5. Business Continuity Management Program
In accordance with TBS requirements, federal departments must establish a BCM Program which is composed of four elements:
- The establishment of BCM Program governance
- The conduct of a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- The development of BCPs and arrangements
- The maintenance of BCM Program readiness
5.1. BCM Program Governance
To address the requirements of the Policy on Government Security and the TBS Operational Security Standard – Business Continuity Planning (BCP) Program, it is essential for Senior departmental managers commit to the BCM Program and:
- Integrate the BCM Program into a strategic planning framework
- Ensure that the BCM Program is in compliance with government policy
- Ensure that the BCM Program is expertly reviewed by the department
- Appoint participants to the BCM Program
Governance of the BCM Program across the ESDC Portfolio consists of BCP Owners: Assistant Deputy Ministers (ADMs), Directors General (DGs) and Directors; and a BCP Owner Support Team: The Emergency Management and Business Continuity (EMBC) Division representing the Director of the EMBC Division, Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators (appointed by the ADMs), and the IT Continuity Coordinator (appointed by the Department’s Chief Information Officer).
According to the PGS, the Chief Security Officer (CSO) is to direct and coordinate the Chief Security Program (CSP), which includes the Departmental BCP.
ESDC’s BCM Program Organization structure is shown in Figure 1:
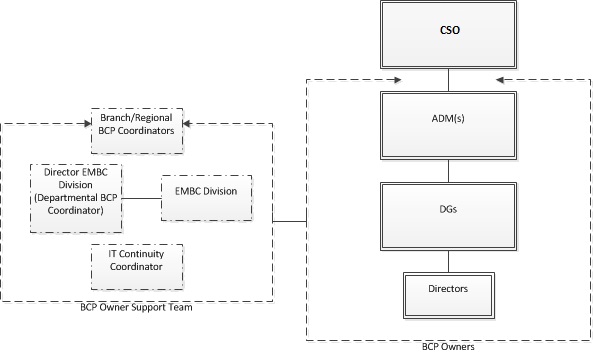
Figure 1: ESDC’s BCM Program Organization Structure Long Description
Figure 1: An organizational chart showing BCP Owners (CSO, ADMs, DGs, and Directors) and the BCP owner support team (Branch/Regional BCP coordinators, the Director of the EMBC Division, the EMBC Division and the IT continuity Coordinator).
- Branch and regional BCP Coordinators must be of the appropriate level and be provided with the required training to fulfill the responsibilities of their role.
- The Director of the EMBC division serves as ESDC’s Departmental BCP Coordinator.
5.1.1. Departmental Enablers
ESDC’s has five departmental enablers who provide expertise related to their businesses (Table 1). These enablers must be consulted when conducting BIA’s and creating any BCP
Table 1: Departmental Enabler
Innovation, Information and Technology Branch (IITB)
Expertise: Information Management and Information Technology
Chief Financial Officer Branch (CFOB)
Expertise: Finance / Accommodations
Public Affairs and Stakeholder Relations Branch (PASRB)
Expertise: Communications
Integrity Services Branch (ISB)
Expertise: Emergency and Security
Human Resources Services Branch (HRSB)
Expertise: Human Resources
Business continuity management is dependent on IT continuity management, whose responsibility belongs to IITB. As such, ESDC’s Chief Information Officer (CIO), ADM of IITB, is responsible for designating an IT Continuity Coordinator who collaborates with the EMBC Division to mutually obtain an understanding of which IT services are necessary to support the Department’s critical services and activities.
5.2 Business Impact Analyses
BIAs are the foundation from which BCPs are developed. BIAs are conducted to determine the nature of the department’s business and the direct and indirect impacts of disruptions to the department. Most importantly, BIAs identify internal/external dependencies (including IT) and prioritize critical services.
A Companion Guide for the Business Impact Assessment Questionnaire has been developed by the EMBC Division. Directors should use this guide, in conjunction with the other BIA materials in the EMBC Portal: Business Continuity Management, to complete their BIAs.
The roles and responsibilities of BCP Owners and the BCP Owner Support Team regarding BIAs are outlined in Table 2:
Table 2: BIA Roles and Responsibilities
Directors Responsibilities
- Complete their unit’s BIA Questionnaire using the BIA toolbox within system applications to improve consistency of BIAs across the Department.
- Liaise with partners (Branches, Regions, stakeholders) as necessary to address dependencies.
- Store the document in a centralized database provided by the EMBC Division for critical service.
- Submit completed BIA to their DG for review and approval.
- Review and update their BIA as required. (E.g. when there is a change in BIA questionnaire responses)
DGs Responsibilities
- Recommend BIA questionnaire results.
ADMs Responsibilities
- Approve BIA questionnaire results.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Coordinate BIA completion across their respective Branch/Region.
- Support Directors in the completion of BIAs.
- Submit ADM approved tracking sheet to the EMBC Division.
IT Continuity Coordinator Responsibilities
- In coordination with the EMBC Division, conducts risk assessments and supports the completion of the BIA questionnaire to obtain an understanding of the critical IT services/applications necessary to support the department’s critical services and activities.
- Assess and determine critical IT service/application Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) for new IT services/applications to support the Department’s critical services and activities. See Note for RPO definition.
- Maintains the official Departmental list of critical IT services/applications and their respective RTOs and RPOs.
- Supports businesses (i.e. Directors) in identifying variances between IT service/application RTOs and program/service RTOs.
- Supports businesses (i.e. Directors) in determining critical IT services/applications and their respective RTOs and RPOs.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Provide functional guidance and direction to BCP Owners and Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators.
- Establish working groups as necessary.
- Coordinate the completion of BIAs throughout the Department.
- Review data collected from BIA questionnaires against approved criteria of business function.
- Identify and resolve misclassifications, i.e. where services/programs are incorrectly assessed as critical or non-critical.
- Identify gaps (operational, strategic, financial, etc.) and seek clarification.
- Summarize Departmental interdependencies and supply chain as identified through BIAs.
- Establish the Departmental list of critical services in collaboration with Branches/Regions.
- Oversee the prioritization of critical services.
- Obtain Corporate Management Committee (CMC) approval of the prioritized Departmental critical services list.
- Prepare and present final Departmental BIA results to the CMC.
- ESDC uses a BIA questionnaire (available in the BIA Toolbox) to conduct its Branches’ and Regions’ BIAs.
- BIAs are conducted at the Director level in collaboration with Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators.
- BIAs must be conducted in collaboration with stakeholders and partners to foster resilience, department wide consistency and to reduce the duplication of work across critical services.
- An RPO is the point in time of the last good back up offsite at the time of the disaster. This identifies the maximum amount of data loss the Department is willing to accept during an event.
5.2.1. Prioritization of Critical Programs/Services
For the Department, Strategic and Service Policies Branch (SSPB) advises Treasury Board Secretariat (TBS) on the departmental programs and services that ESDC will provide. EMBC conducts an analysis of the collective BIA questionnaires and presents recommendations on departmental critical services and programs. The CMC, reviews this proposal, and offers endorsement of ESDC’s critical services and programs. In parallel Human Resource Services Branch (HRSB) conducts a review, and makes recommendations on essential services. These are also presented to CMC for endorsement. Priority is assigned based on:
- Minimum Service Levels (MSLs): the level of service delivery that is essential to avoid a high degree of injury, and that is maintained until full recovery.
- Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs): the targeted amount of time between the time of impact and the time when the process is operating at the minimum acceptable level.
- Periods of Criticality.
- Interdependencies
- Whether the program/service responds directly to a departmental area of responsibility under the Federal Emergency Response Plan:
- ESF 7 – Human and Social Services (ESDC is the Primary Department)
- ESF 11 – Logistics Operations Management (ESDC is a Supporting Department)
- ESF 12 – Public Communications (ESDC is a Supporting Department)
- Impacts of the disruption:
- Health of Canadians
- Safety of Canadians
- Security of Canadians
- Economic Well-Being of Canadians
- Function of ESDC/Government
- Public Confidence/Reputation
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance of ESDC
5.3. BCP Development and Arrangements
A BCP is a set of documented processes, procedures, strategies and contact information required for the continued delivery of critical services or products (including IM and IT) to Canadians during a disruption within acceptable timeframes.
A Companion Guide for the Business Continuity Plan Template has been developed by the EMBC Division. BCP Owners should use this guide, in conjunction with the BCP materials in the EMBC Portal: Business Continuity Management, to complete their BCPs.
5.3.1. Branch/Regional BCP Development
The roles and responsibilities of BCP Owners and the BCP Owner Support Team in Branch/Regional BCP development are outlined in Table 3:
Table 3: BCP Development Roles and Responsibilities
BCP Owners Responsibilities
- Identify, develop and recommend solid response and recovery strategies for each critical function.
- Liaise with other partners (branches, regions, stakeholders) as necessary to address dependencies.
- Assess each recovery strategy in terms of possible disruption, impacts on the department, benefits, risks, feasibility and cost (in collaboration with financial authorities) to select the most appropriate option.
- Details of benefits, risks, feasibility and costs must be provided for each selected recovery strategy.
- Engage with internal partners and external stakeholders to validate and support the proposed recovery strategies.
- Complete the BCPs based upon the results and approval of their respective BIA using the Departmental automated BCP Template which includes:
- Cover page (BCP Type, BCP owner, year, program, BCP owner, etc.)
- Profile (description of activities, building information, critical services summary, etc.)
- Action plan to activate the BCP
- BCP activation and recovery checklist
- Communications Strategy
- Organizational diagram for the Crisis Management Team
- Critical business functions/services and recovery strategies
- Non-critical business functions/services
- List of internal emergency critical personnel.
- Alternate work site locations for DM/ADM, BCP team, critical staff and critical operations
- List of partners, stakeholders, suppliers/contractors and emergency contacts.
- Staff contact list
- 3-Deep Organizational Structure.
- BCP incident and action log
- BCP document log
- Obtain approval for their BCP.
Directors' Responsibilities
- Submit their BCP for DG review and approval.
DGs Responsibilities
- Review their Directors’ response and recovery strategies.
- Assess recovery strategies for feasibility and if issues are adequately resolved.
- Approve their Directors’ BCPs.
- Roll-up their Directors’ BCPs into their respective BCP.
- Submit their BCP for ADM review and approval.
ADMs Responsibilities
- Approve their DGs’ BCPs.
- Roll-up each DGs BCP into their respective BCP.
- Provide the BCPs to their Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators.
- Support the continuity and delivery of programs and services for which they are the lead, by:
- Tasking the development of an in-depth horizontal business continuity plan for each critical program or service as approved by the CMC.
- Oversee the planning for the continuity and recovery of operations.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Create an organizational diagram for their Branch/Regional Crisis Management Team
- Support Directors with the development of BCPs.
- Support DGs and ADMs during the roll-up process.
- Coordinate the completion of all BCPs, including the roll-ups at the DG and ADM level.
- Submit the completed and approved BCPs to the EMBC Division.
IT Continuity Coordinator Responsibilities
- Support the EMBC division, Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators and IT specialists in the development of BCPs.
- Recovery strategies for IT operations.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Support the development of BCPs.
- Provide functional guidance and direction.
- Coordinate the integration of IM, IT, and other continuity plans and arrangements into the BCM Program.
- Establish working groups as necessary.
- Analyze the response and recovery strategies submitted by branches and regions.
- Identify gaps and seek clarification as required.
- Report and present on Departmental BCP results and status to corporate committees.
- Obtain corporate committee approval.
5.3.2. BCP Roll-Up
Once completed, Director BCPs are rolled-up to create DG BCPs and DG BCPs are rolled-up to create ADM BCPs. When rolling-up their BCPs, DGs and ADMs should seek to reduce the content of their BCPs to essential information/contacts for each of their respective critical service. This is done to simplify emergency response. Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators and the EMBC Division are tasked to support their respective DGs and ADMs throughout the Branch/Regional BCP roll-up process.
Information from ADM BCPs are rolled up horizontally with respect to their critical services into Horizontal BCPs using the process described in Section 5.4.
Figure 2 outlines the BCP roll-up from Director BCPs to Horizontal BCPs:
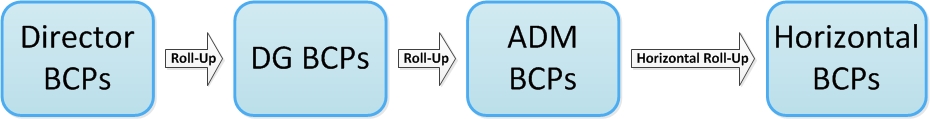
Figure 2: BCP Roll-Up Long Description
Figure 2: The roll up progression from Director level BCPs to DG level BCPs and ADM level BCPs which, through a Horizontal Roll-Up, become Horizontal BCPs.
5.3.3. IT Continuity
IT Continuity Planning underpins BCP strategies, describing how continuity of IT operations are ensured for disaster events affecting IT. IT Continuity planning refers to planning and measures to recover information system services after a disruption, similar to BCPs. The recovery of IT services/applications are often the driving factor for the recovery of ESDC’s critical services and programs and therefore must be integrated into BCP strategies.
The roles and responsibilities of BCP Owners and the BCP Owner Support Team in IT Continuity are outlined in Table 4:
Table 4 : IT Continuity Roles and Responsibilities
IT Continuity Coordinator Responsibilities
- Create an IT Crisis Management Plan to support response and recovery in of a major IT outage.
- Support technical IT Teams in the development of technical recovery plans for critical IT services/applications.
- Communicate and supply IT Crisis Management Plan and technical recovery plans to BCP owners as appropriate.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Coordinate between BCP Owners and IT Continuity Coordinator, as required
5.4. Horizontal BCPs
Horizontal BCPs for all critical programs/services are required to establish ESDC’s Departmental BCP. Rather than being developed for individual branches or regions, Horizontal BCPs are developed by combining ADM BCPs across critical programs/services in collaboration with all stakeholders related to/dependent on the critical program/service’s delivery. The benefits of the service-based horizontal approach to BCP development are to:
- Improve response times when faced with a crisis situation
- Improve reporting accuracy of delivery support services, dependencies and IT requirements
- Identify clear operational connections; both internal and external dependencies and IT demands
- Provide senior management with accurate and easily accessible information to enable effective decision making
- Improve communication between all partners/stakeholders during a time of crisis
- Improve program operation during a time of crisis
- Provide an end to end view of the program/service.
The Horizontal BCP Owner is defined as the ADM responsible for the critical service/program for which the Horizontal BCP is being developed.
The Horizontal BCP Owner is responsible for the maintenance of their Horizontal BCP as well as leading, overseeing and coordinating Horizontal BCP development.The Horizontal BCP development process is outlined in Figure 3.
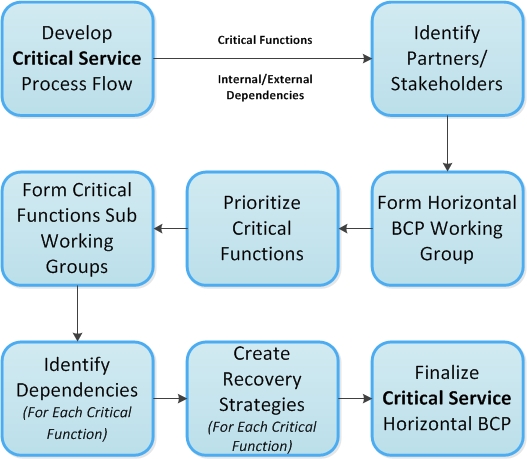
Figure 3: The Horizontal BCP Development Process Long Description
Figure 3: A simplified process map for the development of Horizontal BCPs.
- Develop the process flow of the critical service including:
- Critical Functions
- Internal/External dependencies
- Identify Partners/stakeholders
- Form a Horizontal BCP working group with identified partners/stakeholders
- The horizontal BCP working group prioritizes critical functions
- Critical functions sub working groups are formed from Horizontal BCP working group
- Dependencies for each critical function are identified
- Recovery strategies are created for each critical function
- Recovery strategies for critical functions are consolidated to form the (Critical Service) Horizontal BCP
- Develop the process flow of the critical service including:
The EMBC Division, representing the Director of the EMBC Division as the Departmental BCP Coordinator, is responsible for supporting the development of Horizontal BCPs for each of ESDC’s critical services.
In the event of a change that would impact other interdependent partners and stakeholders, it is critical that Horizontal BCP Owners collaborate and coordinate this change information. For example, if one BCP owner changes an IT tool that will impact partners and stakeholders, they must contact their partners to assess the mutual impact in order to ensure that a continuity of service is maintained.
The key steps in the development of service-based Horizontal BCPs are outlined in the following eight steps:
5.4.1. Step 1: Develop a Critical Service Process Flow
Table 5: Roles and Responsibilities in Developing the Critical Service/Program Process Flow
Horizontal BCP Owner Responsibilities
- Develop a comprehensive process flow of their critical program/service, i.e. all functions required for the delivery of the critical service as well as internal/external dependencies must be represented.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinator Responsibilities
- Primary point of coordination between branches/regions and the EMBC Division.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Review the Horizontal BCP Owner’s process flow.
Critical functions and dependencies are defined in the Horizontal BCP Owner’s BIA.
5.4.2. Step 2: Identify Partners/Stakeholders
Table 6: Roles and Responsibilities in Identifying Partners/Stakeholders
Horizontal BCP Owner Responsibilities
- Identify internal/external partners/stakeholders related to (e.g. responsible for/dependant on/etc.) the delivery of the critical service.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinator Responsibilities
- Coordinate communications between partners/stakeholders and the EMBC Division.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Review the Horizontal BCP Owner’s list of partners/stakeholders.
5.4.3. Step 3: Form a Horizontal BCP Working Group
Table 7: Roles and Responsibilities in Forming a Horizontal BCP Working Group
IT Continuity Roles and Responsibilities
Horizontal BCP Owner Responsibilities
- Appoint members to the Horizontal BCP working group
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinator Responsibilities
- Coordinate communications between members of the Horizontal BCP working group and the EMBC Division
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Oversee the formation of the Horizontal BCP working group
Members appointed to the Horizontal BCP working group must be knowledgeable regarding their entity’s operational procedures, policies and dependencies related to the critical service.
5.4.4. Step 4: Assess/Prioritize Critical Functions
Critical functions/tasks/activities (referred to hereafter as critical functions) are defined as functions/tasks/activities that are essential to the delivery of a critical service. Critical functions require a recovery strategy should their delivery be interrupted.
Table 8: Roles and Responsibilities and Assessing/Prioritizing Critical Functions
Horizontal BCP Working Group Responsibilities
- Determine, standardize and agree on critical functions in the delivery of the critical service.
- Categorize the critical functions according to the Departmental Business Capability Model (DBCM) – Business Architecture.
- Prioritize critical functions
- Identify who is responsible for each critical function
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Provide assistance to DG’s in reviewing and approving the prioritized list of critical functions.
Horizontal BCP Owner Responsibilities
- Compile a prioritized list of critical functions cross-referenced with their:
- Responsible stakeholder (including contact information)
- DBCM Category
- TISMB Business Relationship Management subject matter experts to provide assistance
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Assess the cross-referenced, prioritized critical functions list.
DGs of Partners and Stakeholders Responsibilities
- Review and approve the cross-referenced list of critical functions.
5.4.5. Step 5: Form Critical Function Sub Working Groups
Table 9: Roles and Responsibilities in Forming and Coordinating Critical Function Working Groups
Horizontal BCP Working Group Responsibilities
- Form Critical Function working groups to analyze and plan for the continuity of each critical function.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Coordinate the Critical Function sub working groups.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Support the Critical Function sub working groups as required.
5.4.6. Step 6: Identify Dependencies
Critical functions/tasks/activities (referred to hereafter as critical functions) are defined as functions/tasks/activities that are essential to the delivery of a critical service. Critical functions require a recovery strategy should their delivery be interrupted.
Table 10: Roles and Responsibilities in Identifying Dependencies
Critical Function Sub Working Groups Responsibilities
- For their critical function (in collaboration with subject matter experts), identify:
- Critical applications/software
- Interdependencies
- Feasible recovery time objectives (RTO), confirmed recovery point objectives (RPO)
- All partners/stakeholders agree on RTOs
- Period of criticality
- If processes/arrangements such as Service-level Agreements (SLA) or Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) are in place or should be developed
- Where the critical function is performed (i.e. site or building)
- Site/Building contact information
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Provide assistance to DG’s in reviewing and approving the dependencies.
Horizontal BCP Owner Responsibilities
- Compile the dependencies identified by the Critical Function sub working groups
- Update the cross-referenced critical functions list to include the following for each critical function:
- Dependencies
- Approved RTOs
- Period of criticality
- Locations and contact information where each critical function is being performed
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Assess the cross-referenced critical functions list.
IITB Responsibilities
- Provide resources in the form of subject matter experts to support the critical functions sub working groups.
DGs of Partners and Stakeholders Responsibilities
- Review and approve the list of dependencies provided by the Horizontal BCP Owner.
- For their critical function (in collaboration with subject matter experts), identify:
5.4.7. Step 7: Develop Recovery Strategies
Table 11: Roles and Responsibilities in Developing Recovery Strategies for Horizontal BCPs
Critical Function Sub Working Groups Responsibilities
- For their critical function (in collaboration with subject matter experts):
- Determine potential recovery strategies
- Strategies from ADM BCPs may be used a basis and expanded upon.
- Select the appropriate strategy based on benefit, risk, feasibility and cost.
- Identify minimum and maximum staff levels
- Determine potential recovery strategies
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Provide assistance to DG’s in reviewing and approving the recovery strategies.
Horizontal BCP Owner Responsibilities
- Compile the selected recovery strategies developed by the Critical Function working groups
- Update the cross-referenced critical functions list to include the selected recovery strategies for each critical function
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Ensure the cross-referenced critical functions list is complete and includes (for each critical function):
- Stakeholder responsible for the critical function (including contact information)
- DBCM Category
- IT dependencies
- Approved RTOs
- Period of criticality
- Locations where the critical function is performed (including contact information)
- Approved recovery strategies
DGs of Partners and Stakeholders Responsibilities
- Review and approve recovery strategies related to their area of responsibility.
- For their critical function (in collaboration with subject matter experts):
5.4.8. Step 8: Finalize Horizontal BCP(s)
Table 12: Roles and Responsibilities for Finalizing Horizontal BCPs
Horizontal BCP Working Group Responsibilities
- In collaboration with the EMBC Division:
- Finalize the Horizontal BCP based upon the cross-referenced critical functions list.
- Perform data analytics using the DBCM (heat maps)
- Follow established departmental approval process.
- Distribute the approved Horizontal BCP to all stakeholders
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Provide assistance to the Horizontal BCP working group in finalizing the Horizontal BCP.
DGs of Partners and Stakeholders Responsibilities
- Review and approve the Horizontal BCP (including recovery strategies)
ADMs Responsibilities
- Approve the Horizontal BCP (including recovery strategies)
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Provide assistance to the Horizontal BCP working group in finalizing the Horizontal BCP.
- Submit the final Horizontal BCP to the Corporate Management Committee (CMC) for approval
- In collaboration with the EMBC Division:
5.5. Post-Event Recovery
Following the implementation of recovery strategies to maintain the delivery of critical services, a business must develop and implement a plan to recover to full operation. The responsibility for this recovery falls on BCP Owners, BCP Coordinators and the EMBC Division as outlined in Table 13:
Table 13: Post-Event Recovery Roles and Responsibilities
BCP Owners Responsibilities
- Identify areas requiring recovery, e.g. replacing IT equipment, workstations, etc.
- Develop a recovery plan in collaboration with stakeholders and partners, i.e. Facilities, IT, etc.
- Provide status updates through the EMBC Event Recovery Report.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Assist BCP Owners in the development and implementation of the recovery plan.
- Coordinate the completion of the EMBC Event Recovery Form and its submission to the National Emergency Operations Centre (NC-NEOC-ESDC-CNOU-EDSC-GD)
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Provide guidance and coordination as required.
5.6. BCM Program Readiness and Maintenance
Following the approval of BCPs (Branch/Regional or Horizontal), permanent maintenance cycles must be established for their review and revision, training and awareness, testing and exercising, and monitoring and reporting.
Additionally, at ESDC, the role of the Branch/Regional BCP Coordinator is supported to assist in the coordination of the BCM Program.
5.6.1. Review and Revision
Regular review and revision of BCPs is necessary to account for changes in legislation, critical services, organization, mandate, management, threat environment, stakeholders, dependencies, etc. ESDC requires that a full review of BCPs be performed on an annual basis to support the effective maintenance of ESDC’s overall readiness and incorporate findings and lessons learned from actual events and exercises.
The roles and responsibilities in Review and Revision are outlined in Table 14:
Table 14: BCP Review and Revision Roles and Responsibilities
BCP Owners Responsibilities
- Review and update all key elements of their BCP contact information on a semi-annual basis.
- Review BCPs as required to reflect changes (e.g. legislation, critical services, organization, mandate, management, threat environment, stakeholders, dependencies, etc.).
- Conduct a full review and update of all components found within BCPs annually.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Coordinate the regular review of BCPs with their respective BCP Owners.
- Submit the approved revised BCPs to the EMBC Division.
IT Continuity Coordinator Responsibilities
- Review and update the Departmental List of Critical Applications on an ongoing basis (minimum of once per year).
- Review and update the IT Crisis Management Plan a minimum of once per year.
- Support technical IT Teams in the review of technical recovery plans for critical IT services/applications a minimum of once per year.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Provide guidance to BCP Owners/Coordinators in reviewing their BCPs.
5.6.2. BCP Training and Awareness
Training and awareness of employees is key to the success and integrity of the Departmental BCP. The purpose of training and awareness is to:
- Address specific training needs and operational knowledge requirements to enable Departmental leads, branch and regional senior management, BCP Owners and BCP coordinators to fulfil their business continuity mandates.
- Raise general awareness within the Department on business continuity activities, procedures, policies and overall state of readiness.
The roles and responsibilities in BCP Training and Awareness are outlined in Table 15:
Table 15: BCP Training and Awareness Roles and Responsibilities
BCP Owners Responsibilities
- Train and brief their BCP Team members and associated staff on their respective roles, responsibilities and arrangements as identified within their respective BCP.
- Support Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators and participate in departmental training and awareness activities.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Work in collaboration with EMBC Division to coordinate training activities.
- Coordinate training and awareness for their branch or region.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Lead the development and maintenance of associated directives and supporting materials to promote an integrated approach to emergency and business continuity management.
- Identify functional training and awareness requirements.
- Work in collaboration with College@ESDC and Public Affairs and Stakeholders Relations Branch to develop Departmental awareness and training strategies.
- Develop training and awareness tools.
- Oversee the Departmental delivery of training and awareness activities.
5.6.3. Testing and Exercising
As part of BCP readiness, ESDC is required to test, exercise and validate all plans on a regular basis to reinforce:
- Branch and regional preparedness and ability to respond to an emergency, crisis situation or major incident;
- Continuity of critical functions/services during an emergency or a crisis; and
- Resumption of all activities and return to “normal” day-to-day business following an emergency, crisis situation or major incident.
To satisfy these requirements, ESDC has developed the EMBC Annual Exercise Calendar which establishes requirements for emergency management exercises for all regions and branches in the ESDC Portfolio. The EMBC Annual Exercise Calendar follows a progressive building block approach where exercises are built on increasing levels of difficulty.
Figure 4 outlines the building block approach and the seven types of exercises. See the Departmental Guide to Exercise Planning for a more detailed description of each exercise. Definitions of the steps can be found in the guide on pages 7 and 8.
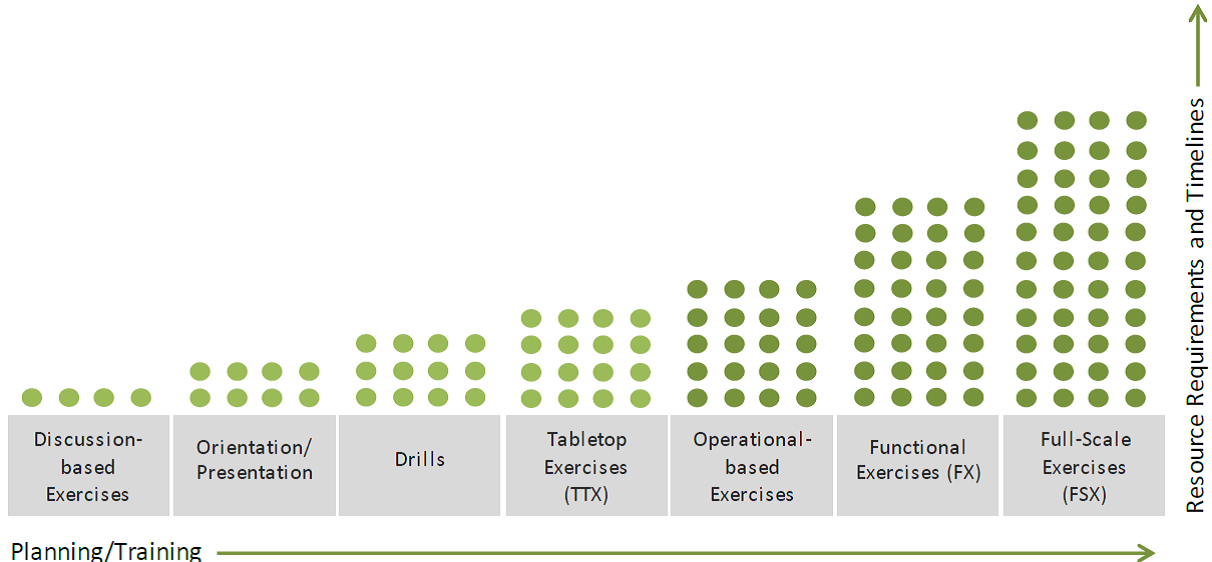
Figure 4: Building Block approach and Exercise Types Long Description
Figure 4: A chart showing the building block approach to emergency exercises (including BCP). The horizontal axis measures Planning and Training commitments while the vertical axis measures Resource Requirements and Timelines.
Beginning from the left, and growing in ascending order, the following exercise types are listed: Discussion-based exercises, Orientation/Presentation, Drills (e.g. evacuations), Tabletop Exercises (TTX), Operational-based Exercises, Functional Exercises (FX) and Full-Scale Exercises (FSX).
The roles and responsibilities in BCP Testing and Exercising are outlined in Table 16:
Table 16: BCP Testing and Exercising Roles and Responsibilities
BCP Owners Responsibilities
- Fill out the EMBC Annual Exercise Calendar.
- Conduct an exercise (as per ESDC’s Departmental Guide to Exercise Planning) of their BCP annually and include any key partners identified in their respective BCP.
- Update BCPs based upon results of the exercise.
- Follow the building block approach and conduct a tabletop exercise (TTX) for more in-depth testing, as required.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Coordinate testing and exercising of their Branch or region BCPs.
- Communicate testing and exercising results to Emergency Management and Business Continuity Division.
IT Continuity Coordinator Responsibilities
- Lead an exercise of the IT Crisis Management Plan annually.
- Support technical IT teams in exercising technical recovery plans for critical IT services/applications annually.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Lead and facilitate departmental exercises every two years.
- Participate in interdepartmental exercises as required.
- Communicate exercise/test results and recommendations to the CMC.
5.6.4. Monitoring and Reporting
Adequate monitoring and reporting is essential to the effectiveness of BCPs and to validate the Departmental state of readiness in responding to major incidents or emergencies while protecting departmental assets and the ability to continue the delivery of service to Canadians.
The roles and responsibilities in BCP Monitoring and Reporting are outlined in Table 17:
Table 17: BCP Monitoring and Reporting Roles and Responsibilities
BCP Owners Responsibilities
- Prepare After Action Reports (AARs) after testing activities or actual events where applicable.
- Report on testing, exercises and actual events via the EMBC annual exercise calendar.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Monitor and report on:
- The completion/approval of BIA questionnaires and submission to the EMBC Division.
- The completion/approval of BCP updates to the EMBC Division.
- The completion of testing and exercising.
- The completion of the BCP Review.
- The delivery and/or completion of training and awareness activities.
- Coordinate the input to the EMBC Annual Exercise Calendar (completed and prospective exercises).
- Maintain the permissions of their BCM SharePoint Sub-sites (e.g. remove access when it is no longer required).
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Monitor BIA questionnaire and BCPs completions.
- Review result and quality of BIA questionnaire and BCPs.
- Provide feedback to branches and regions.
- Share lessons learned and best practices.
- Report on status of BCM Program to senior management on a regular basis.
- Monitor and report on the Department’s compliance with the TBS Standard, policies, programs, plans and related activities.
- Monitor and report on the implementation of the BCM Program as part of the Management Accountability Framework (MAF).
- Coordinate Branch and Region compliance with the EMBC annual exercise calendar.
- Maintain the EMBC Annual Exercise Calendar with information provided by regions and branches.
5.6.5. Branch and Regional BCP Coordinator Support
ESDC’s BCM Program readiness is dependent on the readiness of its Branch and Regional BCP Coordinators. This requires that Branch and Regional BCP Coordinators be:
- Properly trained
- Of the appropriate level to handle the responsibilities of a BCP Coordinator
- Responsible when handing over the position of Branch/Region BCP Coordinator to another individual.
The roles and responsibilities in supporting Branch and Regional BCP Coordinators are outlined in Table 18:
Table 18: Roles and Responsibilities in Supporting Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators
ADMs Responsibilities
- Appoint Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators from a level appropriate to the responsibilities of the position.
Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators Responsibilities
- Attend training sessions provided by EMBC.
- If departing, follow the Branch/Regional BCP Coordinator succession checklist to smooth transition between Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators.
EMBC Division Responsibilities
- Create BCP Coordinator training documentation/tools.
- Conduct BCP Coordinator training on a regular basis.
- Support incoming Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators during onboarding process.
- Keep an updated list of Branch/Regional BCP Coordinators and their contact information.
6. Oversight
The roles and responsibilities in the oversight of the BCM Program are outlined in Table 19:
Table 19: Oversight Roles and Responsibilities
ADMs Responsibilities
- Oversee the implementation of the BCM requirements within their respective branch or region.
DSO Responsibilities
- Oversee that the BCM activities are in alignment with security requirements of the organization and in compliance with Government of Canada’s legislative policies and standards.
- Provide functional guidance and direction on departmental emergency management and business continuity activities, both at the branch and regional levels.
Department Crisis Coordinator (ADM of Integrity Services Branch)
- Oversee the compliance, implementation and review of the BCM Program.
- Oversee the continued development and testing of Horizontal BCPs
7. References
Legislation and guidance relevant to this directive includes the following:
- Emergency Management Act
- Federal Emergency Response Plan
- Policy on Government Security
- Treasury Board Operational Security Standard - Business Continuity Planning (BCP) Program
- Public Safety Canada – A Guide to Business Continuity Planning
- Departmental Strategic Emergency Management Plan
- Standard Operating Procedure For the Departmental Crisis Management Team
8. Enquiries
For supplemental information on this Operational Directive, please refer to the Emergency Management and Business Continuity IntraWeb.
Please direct any questions to the EMBC Division General Inquiry Mailbox at: NC-GUCA-GUCA-GD