Employment Equity Cycle of Activities
Click on the different cycles of the diagram for more information
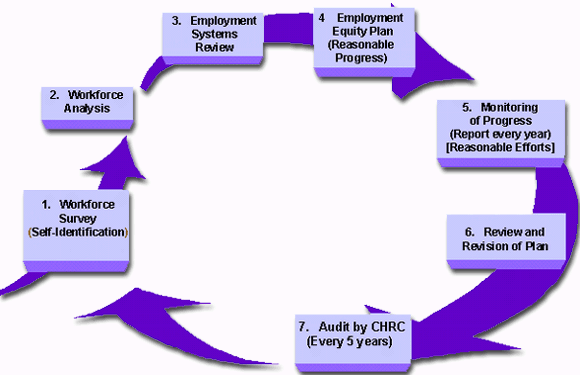
Cycle of Activities
- Self-Identification
- Workforce Analysis
- Employment Systems Review
- Employment Equity Plan
- Monitoring of Progress
- Review and Revision of Plan
- Canadian Human Rights Commission Audit
Ongoing Activities
Cycle of Activities
1. Self-Identification
Knowing the composition of our workforce is the first step to ensuring that women, Aboriginal peoples, persons with disabilities and visible minorities (the designated groups) are employed within the federal public service at the same level as they are represented in the general workforce.
Identifying the make-up of the Department’s workforce is accomplished by asking employees to fill out a survey. This survey is found in myEMS (PeopleSoft)
2. Workforce Analysis
Once employees have completed the self-identification survey, human resources professionals analyze the data. This analysis provides a quick snapshot to enable the Department to identify the gap between the representation of the designated groups in the Department and their representation in the general workforce.
3. Employment Systems Review
When significant gaps exist between the representation of the designated groups in the Department and their representation in the general workforce, this may indicate a barrier to employment.
A barrier to employment is anything that may prevent a person from becoming employed and having a career in the federal public service. For example, discriminatory hiring and promotion practices, a hostile work environment, etc., are considered barriers to employment.
4. Employment Equity Plan
Once barriers have been identified in the work environment, the Employment Equity Act specifies that an Employment Equity Plan must be developed to eliminate these barriers.
5. Monitoring of Progress
As the employer, the Treasury Board Secretariat monitors the progress of departments by asking them to submit an Annual Report updating them on the progress of the Employment Equity Plan.
The Treasury Board Secretariat reports progress on the implementation of employment equity by providing an Annual Report to Parliament every year.
6. Review and Revision of Plan
Every year, employment equity specialists review the action plan and its success in eliminating barriers. If the barriers are eliminated, no further action is taken. If the barriers are not eliminated, the strategy for removing them is reviewed and readjusted. This process is repeated every year until all barriers are removed.
7. Canadian Human Rights Commission Audit
![]() Once every five years, the Canadian Human Rights Commission will audit departments and agencies to determine if they have fully implemented the Employment Equity Act.
Once every five years, the Canadian Human Rights Commission will audit departments and agencies to determine if they have fully implemented the Employment Equity Act.
Ongoing Activities
Communication
The importance of communication at every step of the implementation of the employment equity program can never be emphasized enough. In accordance with the regulations, employers are required to inform employees and their representatives about measures that are being undertaken for the program. This helps all those involved to better understand the principles the program subscribes to and encourages its effectiveness.
Collaboration
The term collaboration is not defined in the Employment Equity Act. Collaboration is an extension of an effective consultation process. Collaboration, for departments and agencies and unions alike, means providing mutual support for ensuring employment equity in the workplace. More specifically, for departments and agencies, collaboration means making reasonable efforts to obtain the support and assistance of the bargaining agents at every step of the employment equity implementation process. For unions, collaboration means making reasonable efforts to support and facilitate the measures taken to ensure employment equity in the workplace.
Consultation
According to the definition of consultation in section 15 of the Employment Equity Act, the employer shall invite its employee representatives “to provide their views concerning…the assistance that the representatives could provide to the employer” on various matters. It is an ongoing process through which bargaining agents are kept informed and through which they are asked for opinions, advice and information to facilitate the implementation of employment equity measures within an organization.
Record keeping
Because the profile of an organization can change rapidly, the employer must maintain up-to-date information on its workforce. The employer must also be able to supply that information quickly and efficiently, while maintaining confidentiality. Proper record keeping allows for the review and correction of mobility trends that are not in keeping with the principles of workplace equity, such as the continual promotion of one group of employees to the detriment of another.